Surfaces
Surfaces in ACSS are reusable background styles that can include images, textures, patterns, or gradients. They provide a powerful way to create consistent, maintainable background designs across your project.
What Are Surfaces?
A surface is a pre-configured background style that you can apply to any element using a utility class. Unlike simple background colors, surfaces can include:
- Background images or textures
- CSS gradients
- CSS patterns
- Background positioning and sizing
- Animation
- Overlay effects
- Automatic color relationship integration
Creating Surfaces
Navigate to Surfaces & Overlays > Custom Surfaces to create up to 5 custom surfaces.
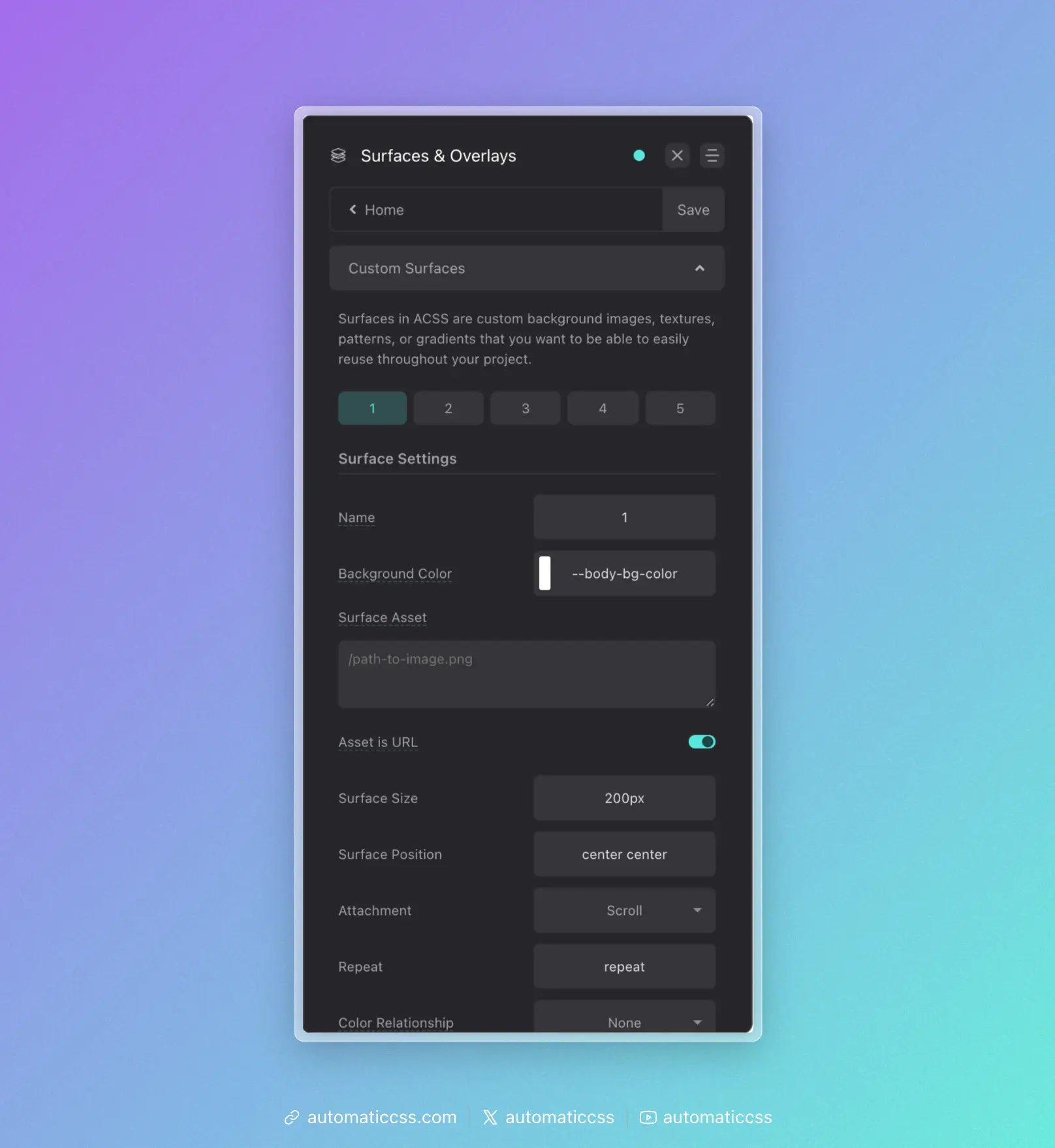
Surface Options
Each surface has the following configuration options:
Main Settings
- Name - Give your surface a descriptive name. This creates a utility class
.surface-{name}(e.g.,.surface-hero,.surface-card). If left as the default number, the class will be.surface-1,.surface-2, etc. - Background Color - A fallback color that displays if your asset has transparency or fails to load.
- Surface Asset - The main visual element of your surface. This can be:
- A URL to an image:
/path/to/image.png - A CSS gradient:
linear-gradient(to right, var(--primary), var(--secondary)) - A CSS pattern or any valid
background-imagevalue
- A URL to an image:
- Asset is URL - Toggle this on if your asset is an image URL (adds the
url()wrapper automatically). - Surface Size - Controls
background-size(e.g.,cover,contain,200px). - Surface Position - Controls
background-position(e.g.,center center,top left). - Attachment - Controls
background-attachment(scroll,fixed,local). - Repeat - Controls
background-repeat(e.g.,repeat,no-repeat,repeat-x). - Color Relationship - Links the surface to the automatic color relationship system.
Color Relationship
The Color Relationship option is powerful. When you select a relationship (ultra-light, light, ultra-dark, or dark), the surface will automatically trigger the same foreground color adjustments as .bg--light, .bg--dark, etc.
For example, if you create a dark textured surface and set its Color Relationship to "dark," any text, headings, links, and icons inside that surface will automatically switch to light colors.
Animation Options
If your surface supports animation (like a moving gradient or animated pattern), you can add CSS animation here:
- Animation - Any valid CSS animation shorthand (e.g.,
gradientMove 10s infinite linear).
Note: You must define the @keyframes for your animation in custom CSS.
Overlay Options
Each surface can have an optional overlay:
- Enable Overlay - Toggle overlay visibility
- Overlay Color - The overlay color
- Overlay Opacity - Control overlay transparency
Using Surfaces
Apply a surface to any element using the generated utility class:
<section class="surface-hero">
<!-- Content here -->
</section>
Or use the CSS variable approach:
.my-element {
background: var(--surface-1);
}
Surfaces vs Background Classes
| Feature | .bg--{color} | .surface-{name} |
|---|---|---|
| Solid colors | Yes | Yes (as fallback) |
| Images/textures | No | Yes |
| Gradients | Yes | Yes |
| Patterns | No | Yes |
| Animation | No | Yes |
| Built-in overlay | No | Yes |
| Color relationships | Yes | Yes |
Use background classes for simple solid color backgrounds. Use surfaces when you need more complex background designs that you want to reuse.
Changes From 3.x
Surfaces are a new feature in ACSS 4.0. They provide a centralized way to manage complex, reusable background styles with full integration into the automatic color relationship system.